Pollination process worksheets.
Pollination process worksheets.
Pollination is a crucial biological process in which pollen, containing male reproductive cells (sperm), is transferred from the male reproductive organs of a flower to the female reproductive organs of the same or a different flower. This process is essential for the fertilization and reproduction of many flowering plants, resulting in the production of seeds and the continuation of plant species. Here’s an overview of the pollination process: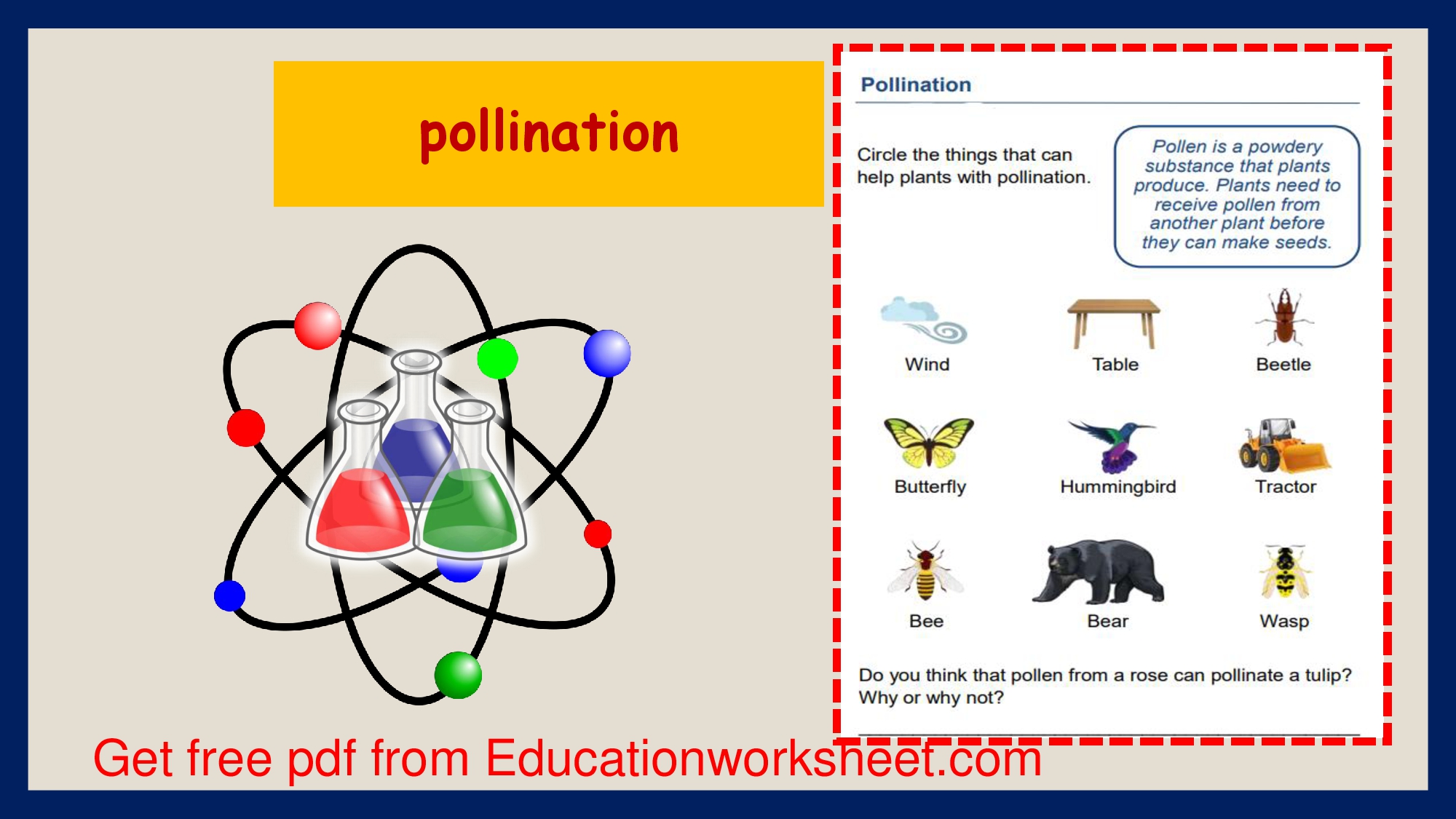
Floral Attraction Pollination process worksheets.
To begin the pollination process, a flower must attract pollinators. Flowers have evolved various mechanisms to achieve this, including vibrant colors, fragrances, and nectar production. These characteristics serve to lure pollinators, which can include insects (such as bees, butterflies, and flies), birds, bats, wind, or even water.
Transfer of Pollen Pollination process worksheets.
When a pollinator visits a flower in search of nectar or other rewards, it brushes against the flower’s reproductive structures. This often results in the transfer of pollen from the anther (the male part of the flower) to the stigma (the female part of the flower).
Insects Pollination process worksheets.
Pollinators like bees and butterflies often have specialized structures, such as pollen baskets and proboscises, which help them collect and transfer pollen as they move from flower to flower.
Birds and Bats Pollination process worksheets.
These larger pollinators may also transfer pollen as they feed on nectar, with the pollen sticking to their bodies or beaks.
Wind Pollination process worksheets.
In some plants, especially those with small, inconspicuous flowers, pollination occurs via the wind. These plants produce lightweight pollen that is carried by the breeze to other flowers.
Pollen Tube Formation:
Once pollen lands on a compatible stigma, it can begin to germinate. The pollen grain sends out a tube (the pollen tube) through the style (the tube-like structure connecting the stigma to the ovary) to reach the ovule (the female gametophyte).
Fertilization:
The pollen tube delivers the male gametes (sperm cells) to the ovule, where fertilization occurs. This results in the formation of a zygote, which will develop into an embryo, and eventually, a seed.
Seed Development:
After fertilization, the ovule develops into a seed. The surrounding ovary often matures into a fruit, protecting and aiding in the dispersal of the seeds.

Fruit Formation:
In many cases, the fertilized ovary transforms into a fruit that encases the seeds. This fruit can be attractive to animals, which consume the fruit and disperse the seeds in their droppings, helping the plant spread to new locations.
Continuation of the Life Cycle:
Once the seeds are dispersed and find suitable conditions for germination, the plant life cycle begins anew, with the potential for the growth of a new plant.
The pollination process is crucial for the reproduction of many plant species, including those that produce fruits, vegetables, and flowers. It also plays a significant role in the ecological relationships between plants and their pollinators, which can include a wide range of animals and even abiotic factors like wind and water.
Pollination is the process that allows plants to reproduce.
Pollination For Kids! In some cases, the wind and rain blows pollen between plants, which causes pollen to transfer to the female reproductive part of the plant. However, most plants need bees and other insects to pollinate from one plant to the next.
The Plant Pollination Process Pollination process worksheets.
- A pollen grain lands on the sticky stigma.
- A pollen tube grows from the pollen grain, and down the style, carrying a male gamete with it down the tube to meet the female gamete in an ovule.
- The male and female gamete fuse and fertilization occurs.
Air, water, animals and insects .
The agents or media which can transfer the pollen grains for pollination are called the agents of pollination. Air, water, animals and insects are the common agents of pollination. Pollination by air: Light and dry pollen grains are carried by air to the other plants.

