Parts of a seed worksheets.
Parts of a seed worksheets.
A seed is a complex structure consisting of several distinct parts, each with a specific function in the process of plant reproduction and growth. The primary parts of a seed include: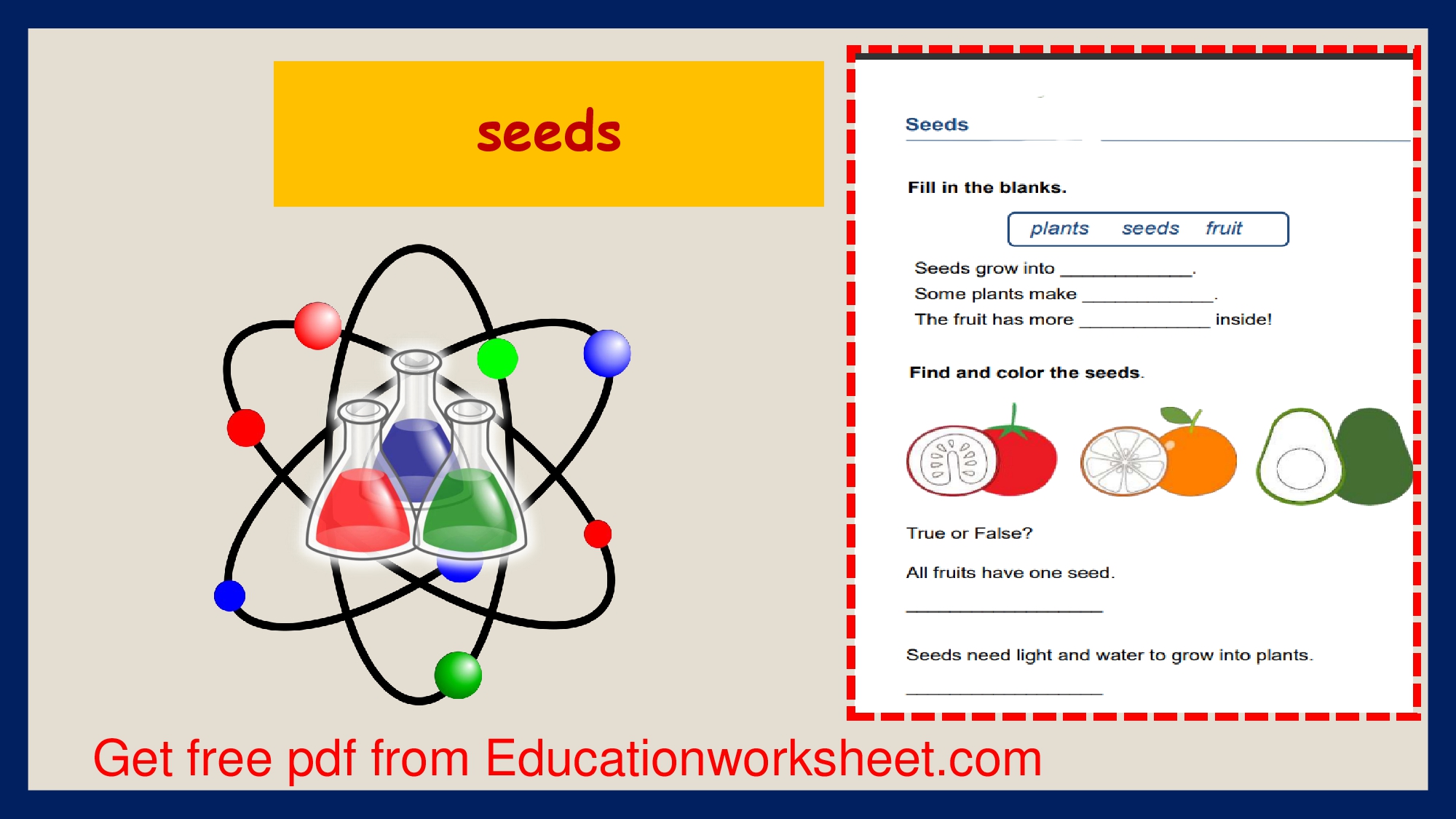
Seed Coat (Testa) Parts of a seed worksheets.
The seed coat is the outer protective covering of the seed. It provides physical protection for the inner parts of the seed and helps prevent desiccation (drying out) and damage. The seed coat can vary in thickness, texture, and color depending on the plant species.
Embryo Parts of a seed worksheets.
The embryo is the miniature, undeveloped plant within the seed. It contains all the essential structures that will give rise to the mature plant, including the shoot system (which will become the stem and leaves) and the root system. The embryo is typically composed of the following parts:
Radicle Parts of a seed worksheets.
The radicle is the embryonic root. It is the first part to emerge during germination and develops into the root system of the mature plant.

Plumule Parts of a seed worksheets.
The plumule is the embryonic shoot. It contains the embryonic leaves and stem, which will develop into the above-ground parts of the mature plant.
Cotyledons Parts of a seed worksheets.
Cotyledons are specialized seed leaves that serve as the initial food source for the developing embryo. Some plants have one cotyledon (monocots), while others have two (dicots).
Endosperm (in some seeds) Parts of a seed worksheets.
The endosperm is a tissue that stores nutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, which are essential for the early growth and development of the embryo. Not all seeds have endosperm, as some rely solely on the cotyledons for nourishment.
Cotyledon (in some seeds) Parts of a seed worksheets.
As mentioned earlier, cotyledons are specialized seed leaves. In some plants, they remain within the seed and continue to provide nutrients to the growing embryo after germination. In others, they emerge above ground and may become the first leaves of the young seedling.
Hilum:
The hilum is a scar on the seed coat where the seed was attached to the parent plant. It is the point through which the seed received nutrients and water from the parent plant.
Micropyle:
The micropyle is a small opening in the seed coat near the hilum. It serves as the point of entry for water and oxygen during germination.
Epicotyl and Hypocotyl (in dicots):
Dicotyledonous plants have two cotyledons, and between them, there is a region known as the hypocotyl, which connects the radicle and the epicotyl. The epicotyl is the upper portion of the embryonic shoot that gives rise to the stem and leaves above the cotyledons.
These various parts work together to ensure the successful germination and growth of a new plant from the seed. The specific structure and characteristics of seeds can vary significantly among different plant species.
Embryo, endosperm, and seed coat.
Most seeds consist of three parts: embryo, endosperm, and seed coat. The embryo is a tiny plant that has a root, a stem, and one or more leaves. The endosperm is the nutritive tissue of the seed, often a combination of starch, oil, and protein.
Embryo, endosperm, and seed coat Parts of a seed worksheets.
The three primary parts of a seed are the embryo, endosperm, and seed coat. The embryo is the young multicellular organism before it emerges from the seed. The endosperm is a source of stored food, consisting primarily of starches. The seed coat consists of one or more protective layers that encase the seed.
A miniature plant, called an embryo Parts of a seed worksheets.
A seed contains a miniature plant, called an embryo, that can develop into a fully grown plant. The outer shell of a seed, called a seed coat, protects the embryo. Inside the seed a nutritious material provides food to the embryo. In flowering plants this material is called endosperm.