parts of plants worksheet.
parts of plants worksheet.
Roots parts of plants worksheet.
The underground part of a plant that anchors it to the soil and absorbs water and nutrients.
Stems parts of plants worksheet.
The above-ground structures that support leaves, flowers, and fruits while also transporting water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Leaves parts of plants worksheet.
The green, photosynthetic organs of the plant responsible for producing food (sugars) through photosynthesis.
Flowers parts of plants worksheet.
Reproductive structures of the plant that produce seeds. They are often colorful and attract pollinators.
Fruits parts of plants worksheet.
Structures that develop from the ovaries of flowers and contain seeds. Fruits come in various shapes, sizes, and flavors.
Seeds parts of plants worksheet.
Reproductive units that can grow into new plants. Seeds are often found within fruits.
Buds parts of plants worksheet.
Undeveloped or dormant shoots that can grow into new stems, leaves, or flowers.
Tubers parts of plants worksheet.
Thickened, underground stems used for storing nutrients and reproducing new plants. Examples include potatoes.
Bulbs
Underground storage organs consisting of modified leaves and stems. Onions and tulips are examples of bulb plants.
Corms:
Swollen, underground stems that store energy and can produce new shoots. Taro is an example of a corm.
Rhizomes:
Horizontal, underground stems that give rise to new shoots and roots. Ginger is an example of a rhizome.
Thorns and Spines:
Modified stems or leaves that serve as defensive structures against herbivores.
Bark:
The protective outer covering of woody plants, consisting of dead cells. It helps protect against environmental factors and pests.
Sap:
The liquid or fluid found in various plant parts, often containing nutrients, sugars, or resins.
Nectar:
A sugary fluid produced by flowers to attract pollinators like bees and butterflies.
Pollen:
Fine, powdery grains produced by male parts of flowers that fertilize the female parts, enabling seed production.
Trichomes:
Hair-like structures on plant surfaces that can serve various functions, including protecting against herbivores and reducing water loss.
Cuticles:
Waxy, protective layers on the surface of leaves and stems that help reduce water loss.
Vascular Tissues:
Specialized tissues, including xylem and phloem, that transport water, nutrients, and food throughout the plant.
Lenticels:
Pores or small openings on stems and woody tissues that allow for gas exchange between plant cells and the external environment.
These various plant parts serve different functions, from support and nutrient storage to reproduction and defense, contributing to the diversity and adaptability of plant life.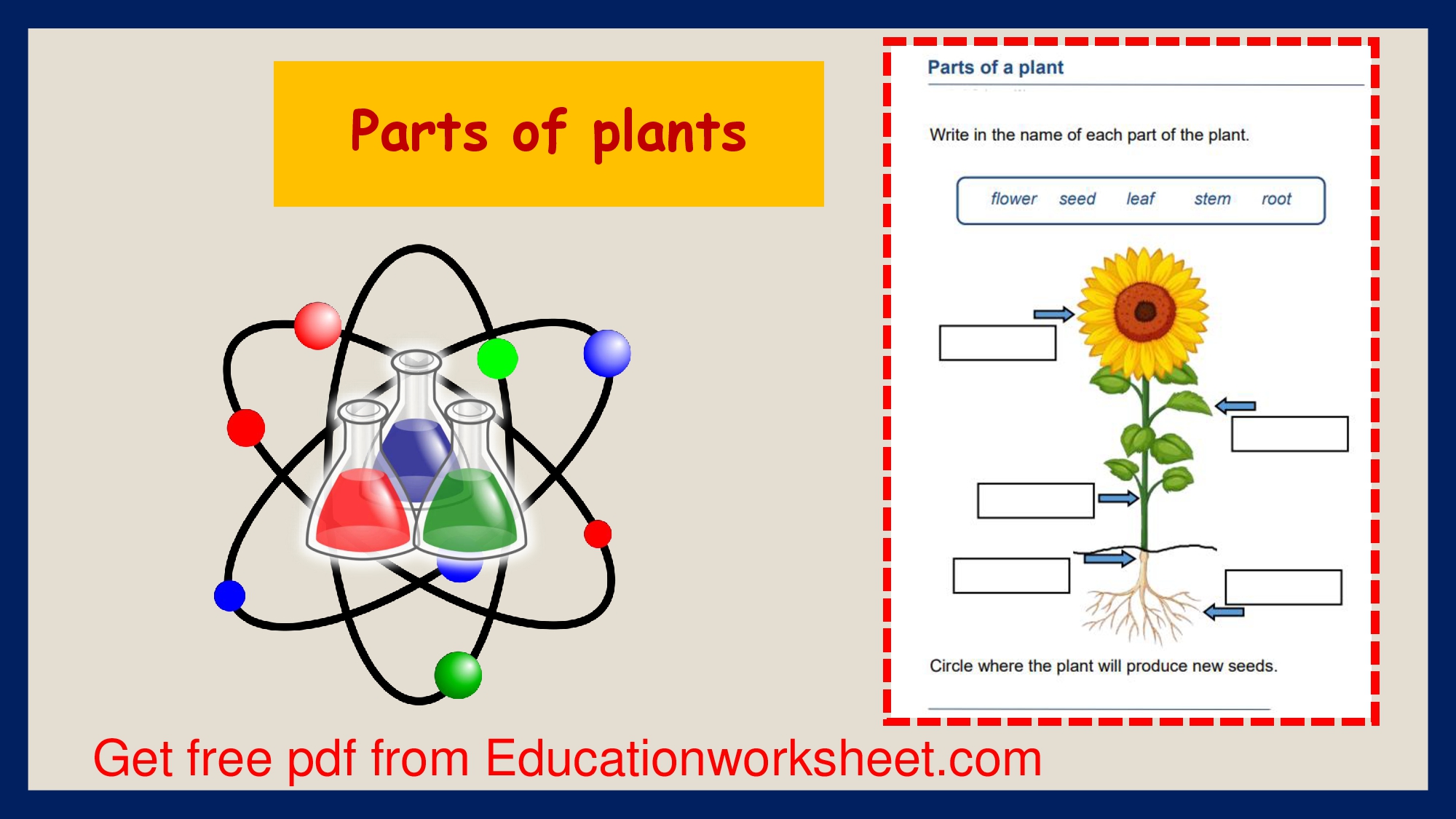
The roots, the leaves, and the stem.
The three main parts are: Each part has a set of jobs to do to keep the plant healthy. The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and anchor the plant in the ground. The stem supports the plant above ground, and carries the water and minerals to the leaves.
Telp the transport water, sugar and nutrients to the leaves and canopy (crown) of the tree.
Branches- Grow from the trunk of the tree and They also help support the leaves that make up the canopy (crown). Leaves-Grow from the stem which are attached to the branches to make up the canopy (crown) of the tree.
Plants are multicellular organisms in the kingdom Plantae that use photosynthesis to make their own food. There are over 300,000 species of plants; common examples of plants include grasses, trees, and shrubs. Plants have an important role in the world’s ecosystems.
The different parts of a plant include roots, stems, leaves, flowers, seeds, and fruits. Roots have the function of absorbing water and minerals from the soil whereas the primary functions of stems are supporting, transporting, storing, and reproducing.The basic parts of most land plants are roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds. The function of each plant parts is described below.
Gases enter leaves through thousands of tiny pores called stomata (sing. stoma).
In most plants these are found on the underside of leaves, where they’re hidden from strong sunlight and protected from dust.

